Prenatal Chromosome Testing
Clinical Indications for Chromosome Analysis
- Advanced maternal age
- Previous child or pregnancy with chromosomal abnormality
- Family history of chromosomal abnormality
- Abnormal ultrasound
- Abnormal maternal serum screen
- Abnormal noninvasive prenatal test (NIPT) result in pregnancy
- Fetal demise
Samples For Prenatal Chromosome Diagnosis
- Amniotic Fluid
- Chorionic Villi
Reference Laboratory Send Out
A portion of the specimen with or without cultured cells can also be sent out to reference laboratories for DNA or Biochemical analysis for specific disorders if required.
Chromosome Analysis Of Amniotic Fluid
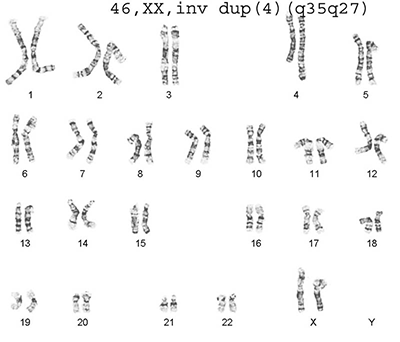
Chromosome analysis of amniotic fluid involves a short-term culture of specimens to provide an optimal number of metaphase cells for determination of chromosomal abnormalities. Microscopic examination of both chromosome number and structure is performed. Examination of 20 metaphases, or 15 clones if available, is routinely performed and additional metaphases will be studied when indicated. At least 5 cells are fully analyzed, with 3 or more G-banded karyotypes created by computer image analysis on each patient.
Chromosome Analysis Of Chorionic Villus Sampling
This test, requiring chorionic villus sampling, is an alternative to genetic amniocentesis, and should be offered to women over age 34 years at conception. Chorionic villus sampling is usually performed at 10-13 weeks of gestation and provides earlier prenatal diagnosis than conventional amniocentesis. Cells are cultured until an adequate number are available for analysis. Microscopic examination of both chromosome number and structure is performed. Routinely, analysis of at least 5 cells and examination of 20 metaphases is performed with additional metaphases studied when indicated. Three or more G-banded karyograms are created by computer image analysis on each patient.
Turnaround time varies from 7-14 days depending on cell growth and extent of workup.
| Prenatal Diagnosis (K-type and AneuVysion FISH) | |
| Specimen Types | Requirements |
| Chorionic villi Amniotic Fluid |
Minimum 10-15 mg of chorionic villus tissue in a sterile tube containing culture medium, sterile saline or balanced salt solution
(Larger samples required if multiple tests are requested)
Minimum 20cc of the fluid |
Requirements Document and Requisition Form
Use Adobe Acrobat to print the PDF forms.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Conventional cytogenetic analysis is capable of detecting structural and numerical chromosomal abnormalities in prenatal samples at the 450 G-banded level. Cryptic imbalances including microdeletions and microduplications cannot be detected by conventional chromosome analysis. In addition, conventional cytogenetic analysis requires dividing cells for metaphase preparation.
Prenatal Chromosome Testing
Clinical Indications for Chromosome Analysis
- Advanced maternal age
- Previous child or pregnancy with chromosomal abnormality
- Family history of chromosomal abnormality
- Abnormal ultrasound
- Abnormal maternal serum screen
- Abnormal noninvasive prenatal test (NIPT) result in pregnancy
- Fetal demise
Samples For Prenatal Chromosome Diagnosis
- Amniotic Fluid
- Chorionic Villi
Reference Laboratory Send Out
A portion of the specimen with or without cultured cells can also be sent out to reference laboratories for DNA or Biochemical analysis for specific disorders if required.
Chromosome Analysis Of Amniotic Fluid
Chromosome analysis of amniotic fluid involves a short-term culture of specimens to provide an optimal number of metaphase cells for determination of chromosomal abnormalities. Microscopic examination of both chromosome number and structure is performed. Examination of 20 metaphases, or 15 clones if available, is routinely performed and additional metaphases will be studied when indicated. At least 5 cells are fully analyzed, with 3 or more G-banded karyotypes created by computer image analysis on each patient.
Chromosome Analysis Of Chorionic Villus Sampling
This test, requiring chorionic villus sampling, is an alternative to genetic amniocentesis, and should be offered to women over age 34 years at conception. Chorionic villus sampling is usually performed at 10-13 weeks of gestation and provides earlier prenatal diagnosis than conventional amniocentesis. Cells are cultured until an adequate number are available for analysis. Microscopic examination of both chromosome number and structure is performed. Routinely, analysis of at least 5 cells and examination of 20 metaphases is performed with additional metaphases studied when indicated. Three or more G-banded karyograms are created by computer image analysis on each patient.
Turnaround time varies from 7-14 days depending on cell growth and extent of workup.
| Prenatal Diagnosis (K-type and AneuVysion FISH) | |
| Specimen Types | Requirements |
| Chorionic villi Amniotic Fluid |
Minimum 10-15 mg of chorionic villus tissue in a sterile tube containing culture medium, sterile saline or balanced salt solution
(Larger samples required if multiple tests are requested)
Minimum 20cc of the fluid |
Requirements Document and Requisition Form
Use Adobe Acrobat to print the PDF forms.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Conventional cytogenetic analysis is capable of detecting structural and numerical chromosomal abnormalities in prenatal samples at the 450 G-banded level. Cryptic imbalances including microdeletions and microduplications cannot be detected by conventional chromosome analysis. In addition, conventional cytogenetic analysis requires dividing cells for metaphase preparation.