Postnatal Microarray Testing
Microarray-based Comparative Genomic Hybridization (aCGH) is a new genetic test that can detect both unbalanced genomic alterations usually identified by chromosome analysis (karyotyping) and unbalanced genomic alterations that cannot be identified by karyotyping (including microdeletions and microduplications and many single gene deletions or duplications). CGH+SNP microarrays can simultaneously detect copy number changes as well as copy neutral aberrations, such as absence of heterozygosity (AOH) and uniparental disomy (UPD).
We provide whole genome aCGH, CGH+SNP, and high resolution X-chromosome (X-HR) microarray analyses.
Whole Genome CGH+SNP Analysis
Clinical Indications For Postnatal aCGH Analysis
- Patient with unexplained intellectual disability
- Developmental delay
- Unusual physical characteristics
- Multiple congenital anomalies
- Suspected gene deletion or duplication
- Autism
- Seizures
- Growth failure
- Hyperactivity
- Patient with suspected UPD/conditions associated with imprinting (i.e., Silver-Russell Syndrome, Maternal UPD 14 Syndrome, Prader-Willi/Angelman Syndrome, Transient neonatal diabetes, Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome, Pseudohypoparathyroidism)
- Autosomal recessive condition due to suspected common ancestry or consanguineous family
- Identification of parental origin of the chromosomal abnormality by trio analysis
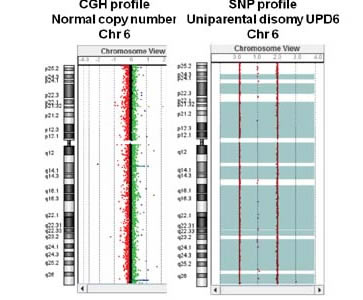
Platform For CGH+SNP Analysis
We use Agilent’s SurePrint G3 CGH+SNP microarrays (4x180K ISCA design) platform. The 110,712 (CGH) oligo probes and 59,647 (SNP) probes with 25.3 kb overall median probe spacing are throughout the genome and with 5 kb in ISCA regions. This platform is designed based on UCSC hg19 (NCBI Build 37, Februry 2009).
High Resolution X-chromosome Microarray Analyses (X-HR)
Clinical Indication For Postnatal X-HR Analysis
CLINICAL INDICATION FOR POSTNATAL X-HR ANALYSIS- Clinical manifestation of X chromosome contiguous gene deletion/duplication syndrome
- X marker/ring chromosome-breakpoint analysis
- Multiple congenital anomalies in patients with X;autosome translocations
- Female carrier status of X chromosome deletion/duplication
- Suspected X-linked genetic disorder
- Premature ovarian failure
- Disorder of sexual development/XY female
Platform For X-HR Analysis
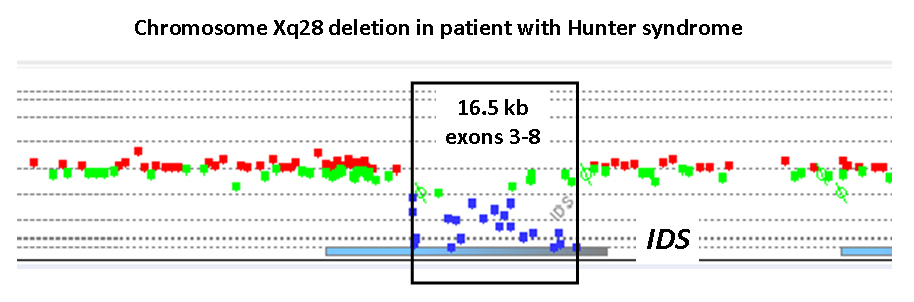 We use the Agilent 180K oligonucleotide array platform specifically designed and validated by Pittsburgh
Cytogenetics Laboratory for the X-chromosome disorders. The 180,000 oligonucleotides on the X-HR chip cover
entire X-chromosome genome with high density probes in the regions containing genes involved in X-chromosome
disorders or associated with premature ovarian failure, as well as some autosomal genes involved disorders of
sexual differentiation. The maximum probe spacing is one probe for every 1 Kb throughout the X-chromosome
genome and one probe for every 0.3-0.5 Kb in the regions containing genes.
We use the Agilent 180K oligonucleotide array platform specifically designed and validated by Pittsburgh
Cytogenetics Laboratory for the X-chromosome disorders. The 180,000 oligonucleotides on the X-HR chip cover
entire X-chromosome genome with high density probes in the regions containing genes involved in X-chromosome
disorders or associated with premature ovarian failure, as well as some autosomal genes involved disorders of
sexual differentiation. The maximum probe spacing is one probe for every 1 Kb throughout the X-chromosome
genome and one probe for every 0.3-0.5 Kb in the regions containing genes.
Samples For Microarray Analysis
DNA extracted from peripheral blood will be used for microarray testing. DNA can also be extracted from skin samples for the test.
Advantages And Limitations For The Tests
CGH-SNP can:
- detect chromosome imbalances identified by classical chromosome analysis
- detect chromosome imbalances that cannot be identified by chromosome analysis
- simultaneously and rapidly evaluate thousands of loci for copy number imbalances
- further characterize the chromosome imbalances detected by karyotyping (e.g., maker chromosomes)
- detect absence of herozygosity (AOH) and uniparental isodisomy (UPD)
- detect polyploidies
aCGH cannot detect:
- balanced rearrangements (e.g., balanced translocation, inversion), polyploidies
- base pair mutations
- gains or losses in the regions of the genome not covered by array
- low level mosaicism (<20%)
Postnatal Microarray Testing
Microarray-based Comparative Genomic Hybridization (aCGH) is a new genetic test that can detect both unbalanced genomic alterations usually identified by chromosome analysis (karyotyping) and unbalanced genomic alterations that cannot be identified by karyotyping (including microdeletions and microduplications and many single gene deletions or duplications). CGH+SNP microarrays can simultaneously detect copy number changes as well as copy neutral aberrations, such as absence of heterozygosity (AOH) and uniparental disomy (UPD).
We provide whole genome aCGH, CGH+SNP, and high resolution X-chromosome (X-HR) microarray analyses.
Whole Genome CGH+SNP Analysis
Clinical Indications For Postnatal aCGH Analysis
- Patient with unexplained intellectual disability
- Developmental delay
- Unusual physical characteristics
- Multiple congenital anomalies
- Suspected gene deletion or duplication
- Autism
- Seizures
- Growth failure
- Hyperactivity
- Patient with suspected UPD/conditions associated with imprinting (i.e., Silver-Russell Syndrome, Maternal UPD 14 Syndrome, Prader-Willi/Angelman Syndrome, Transient neonatal diabetes, Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome, Pseudohypoparathyroidism)
- Autosomal recessive condition due to suspected common ancestry or consanguineous family
- Identification of parental origin of the chromosomal abnormality by trio analysis
Platform For CGH+SNP Analysis
We use Agilent’s SurePrint G3 CGH+SNP microarrays (4x180K ISCA design) platform. The 110,712 (CGH) oligo probes and 59,647 (SNP) probes with 25.3 kb overall median probe spacing are throughout the genome and with 5 kb in ISCA regions. This platform is designed based on UCSC hg19 (NCBI Build 37, Februry 2009).
High Resolution X-chromosome Microarray Analyses (X-HR)
Clinical Indication For Postnatal X-HR Analysis
CLINICAL INDICATION FOR POSTNATAL X-HR ANALYSIS- Clinical manifestation of X chromosome contiguous gene deletion/duplication syndrome
- X marker/ring chromosome-breakpoint analysis
- Multiple congenital anomalies in patients with X;autosome translocations
- Female carrier status of X chromosome deletion/duplication
- Suspected X-linked genetic disorder
- Premature ovarian failure
- Disorder of sexual development/XY female
Platform For X-HR Analysis
We use the Agilent 180K oligonucleotide array platform specifically designed and validated by Pittsburgh Cytogenetics Laboratory for the X-chromosome disorders. The 180,000 oligonucleotides on the X-HR chip cover entire X-chromosome genome with high density probes in the regions containing genes involved in X-chromosome disorders or associated with premature ovarian failure, as well as some autosomal genes involved disorders of sexual differentiation. The maximum probe spacing is one probe for every 1 Kb throughout the X-chromosome genome and one probe for every 0.3-0.5 Kb in the regions containing genes.
Samples For Microarray Analysis
DNA extracted from peripheral blood will be used for microarray testing. DNA can also be extracted from skin samples for the test.
Advantages And Limitations For The Tests
CGH-SNP can:
- detect chromosome imbalances identified by classical chromosome analysis
- detect chromosome imbalances that cannot be identified by chromosome analysis
- simultaneously and rapidly evaluate thousands of loci for copy number imbalances
- further characterize the chromosome imbalances detected by karyotyping (e.g., maker chromosomes)
- detect absence of herozygosity (AOH) and uniparental isodisomy (UPD)
- detect polyploidies
aCGH cannot detect:
- balanced rearrangements (e.g., balanced translocation, inversion), polyploidies
- base pair mutations
- gains or losses in the regions of the genome not covered by array
- low level mosaicism (<20%)