Postnatal Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) Testing
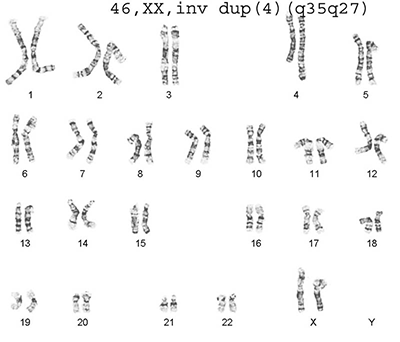 FISH testing is a molecular
cytogenetic analysis that identifies specific chromosomal abnormalities by evaluating
the presence or absence of fluorescence labeled signals in metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei. FISH results
for rapid diagnosis of aneuploidy are typically provided within 24-48 hours from the receipt of the specimen.
FISH testing is a molecular
cytogenetic analysis that identifies specific chromosomal abnormalities by evaluating
the presence or absence of fluorescence labeled signals in metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei. FISH results
for rapid diagnosis of aneuploidy are typically provided within 24-48 hours from the receipt of the specimen.
Specimen Requirements
| Postnatal And Adult Karyotyping FISH | ||
| Specimen Types | Requirements | Turnaround Times |
| Peripheral Blood |
1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) containing 5 cc whole blood For infant or young children: 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep ) containing 1-3 cc whole blood If CGH testing is anticipated later 1 purple top tube (1 x EDTA vacutainer) containing 5cc whole blood is requested |
>2-4 weeks for routine cases 48 hr. verbal preliminary results on STAT analyses; 7 day final report on STAT analyses |
| Postnatal And Adult (CGH or CGH+SNP, FISH and Karyotyping) | ||
| Specimen Types | Requirements | Turnaround Times |
| Peripheral Blood |
1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) and one purple top tube (1XEDTA), each containing 5 cc whole blood For infant or young children: 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) and one purple top tube (1XEDTA), each containing -1-3 cc whole blood 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) containing 5cc whole peripheral blood from each parent |
|
Documents
Use Adobe Acrobat to print the PDF forms.
FISH For aCGH Confirmation
| BAC Probes |
| Whole genomic BAC library is available for aCGH confirmation |
Advantages And Limitations
- FISH testing can rapidly detect and characterize submicroscopic chromosome abnormalities.
- FISH testing has the ability to analyze the abnormalities on metaphase chromosomes from cultured samples as well as interphase cells from specimens that cannot be cultured.
- FISH testing has high sensitivity and specificity.
- The main limitation of FISH analysis is that it only provides information about the specific locus or gene tested.
Postnatal Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH) Testing
FISH testing is a molecular cytogenetic analysis that identifies specific chromosomal abnormalities by evaluating the presence or absence of fluorescence labeled signals in metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei. FISH results for rapid diagnosis of aneuploidy are typically provided within 24-48 hours from the receipt of the specimen.
Specimen Requirements
| Postnatal And Adult Karyotyping FISH | ||
| Specimen Types | Requirements | Turnaround Times |
| Peripheral Blood |
1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) containing 5 cc whole blood For infant or young children: 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep ) containing 1-3 cc whole blood If CGH testing is anticipated later 1 purple top tube (1 x EDTA vacutainer) containing 5cc whole blood is requested |
>2-4 weeks for routine cases 48 hr. verbal preliminary results on STAT analyses; 7 day final report on STAT analyses |
| Postnatal And Adult (CGH or CGH+SNP, FISH and Karyotyping) | ||
| Specimen Types | Requirements | Turnaround Times |
| Peripheral Blood |
1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) and one purple top tube (1XEDTA), each containing 5 cc whole blood For infant or young children: 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) and one purple top tube (1XEDTA), each containing -1-3 cc whole blood 1 green top tube (1 x NaHep) containing 5cc whole peripheral blood from each parent |
|
Documents
Use Adobe Acrobat to print the PDF forms.
FISH For aCGH Confirmation
| BAC Probes |
| Whole genomic BAC library is available for aCGH confirmation |
Advantages And Limitations
- FISH testing can rapidly detect and characterize submicroscopic chromosome abnormalities.
- FISH testing has the ability to analyze the abnormalities on metaphase chromosomes from cultured samples as well as interphase cells from specimens that cannot be cultured.
- FISH testing has high sensitivity and specificity.
- The main limitation of FISH analysis is that it only provides information about the specific locus or gene tested.